Charge number
Charge number or just valance[1] of an ion is the coefficient that, when multiplied by the elementary charge, gives the ion's charge. [2]
For example, the charge on a chloride ion, 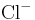 , is
, is 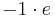 , where e is the elementary charge. This means the charge number for the ion is
, where e is the elementary charge. This means the charge number for the ion is 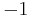 .
.
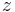 is sometimes used as the symbol for the charge number. In that case, the charge of an ion could be written as
is sometimes used as the symbol for the charge number. In that case, the charge of an ion could be written as 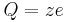 .
.
For an atomic nucleus, which can be regarded as an ion having stripped off all electrons, the charge number is identical with the atomic number Z (number of protons).
In particle physics the charge number is a (derived) flavour quantum number, mostly denoted by Q (regarded as 'electric charge in units of e') rather than z. For color charged particles with like quarks and hypothetical leptoquarks the charge number is a broken multiple of 1/3.
See also
References
- ^ Dynamic Systems in Neuroscience by Izhikevich
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "charge number, z".